Nuts may seem like simple pieces of hardware, but their role in construction, mechanical projects, automotive assembly, and DIY tasks cannot be overstated. Choosing the correct nut ensures the strength, durability, and safety of your assembly. Whether you’re a professional mechanic, engineer, or a DIY enthusiast, understanding the types, sizes, materials, and applications of nuts is essential. This guide will serve as your ultimate reference, helping you make the right choice every time.
What Are Nuts?
A nut is a type of fastener with internal threads that fit onto a bolt, screw, or threaded rod. When paired, nuts and bolts hold components firmly together by creating a strong clamping force. As the bolt passes through materials, the nut threads onto it, securing the assembly. Using the correct nut ensures strength, stability, and long-lasting, safe connections in any project or structure.
Why Nuts Are Important
A nut is a fastener with internal threads that pairs with a bolt, screw, or threaded rod to hold components securely. When threaded onto a bolt, it creates strong clamping force, ensuring stability and safety. Using the right nut prevents loosening, damage, and structural failure, making it essential for any project, from furniture to heavy machinery.
Safety: Properly matched nuts prevent loosening, which could cause accidents.
Strength: Nuts distribute clamping forces evenly when paired with bolts.
Durability: Correct nut selection reduces wear and tear on materials.
Versatility: Different nuts are designed for specific applications, from furniture assembly to heavy machinery.
🔹 Tip: Never underestimate the importance of nuts — the wrong size, material, or type can compromise the entire structure.
Types of Nuts
Nuts are one of the most common and essential fasteners used in mechanical, construction, and DIY projects. They come in a variety of shapes, designs, and materials to suit different applications. Knowing the types of nuts helps you select the right one for your project, ensuring secure, durable, and safe connections. Here’s a detailed overview of the most common types of nuts.
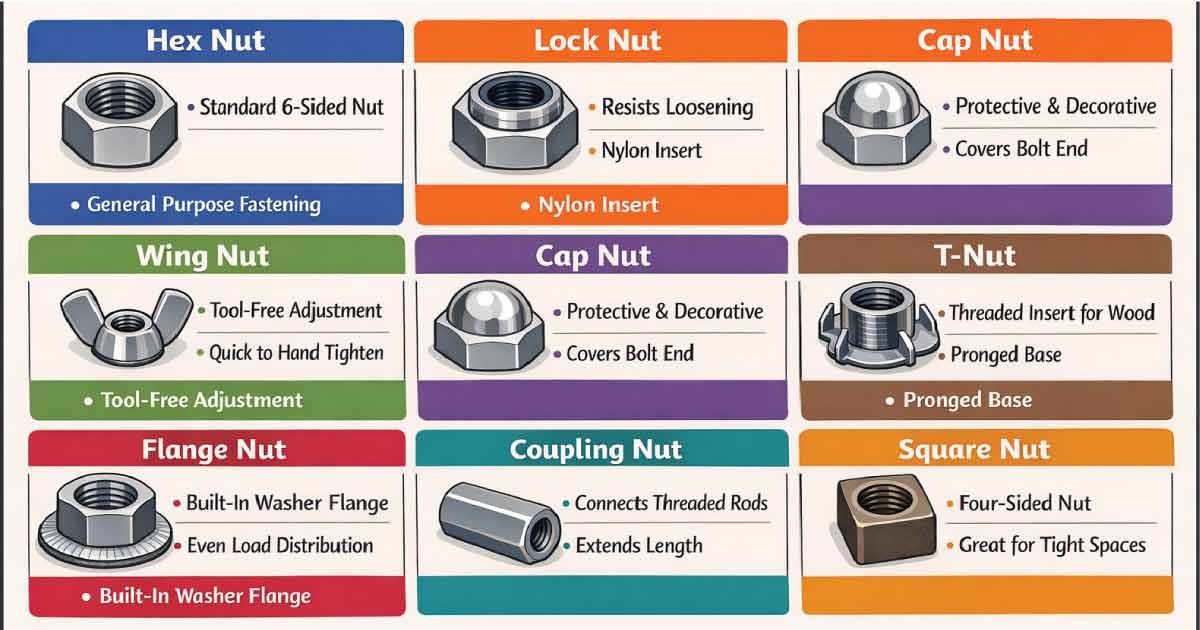
1. Hex Nut
Hex nuts are six-sided fasteners that are widely used in general applications. They are versatile, easy to install, and compatible with most bolts, making them a staple in furniture, machinery, and construction projects. Their hexagonal shape allows for easy tightening with a wrench or socket, providing strong, reliable clamping force that holds components together securely.
-
Shape: Six-sided standard nut.
-
Use: General-purpose fastening; works with most bolts.
-
Applications: Furniture, machinery, construction.
-
Advantage: Easy to tighten with wrench or socket.
2. Lock Nut
Lock nuts are specially designed to resist loosening caused by vibration or movement. They can feature a nylon insert (nyloc) or metal deformation that keeps the nut tight under stress. Lock nuts are commonly used in automotive, machinery, and equipment that experiences constant vibration, preventing accidental loosening and ensuring that assemblies remain secure over time.
-
Shape: Similar to hex, often with nylon insert (nyloc) or metal deformation.
-
Use: Resists loosening under vibration.
-
Applications: Automotive, machinery, vibrating equipment.
-
Advantage: Prevents accidental loosening without additional hardware.
3. Wing Nut
Wing nuts are designed for quick hand tightening, without requiring tools. Their two “wings” make assembly and disassembly fast and easy, which is ideal for applications that need frequent adjustments. Wing nuts are popular in furniture assembly, temporary panels, and equipment covers, providing convenience while maintaining a secure connection.
-
Shape: Two “wings” for hand tightening.
-
Use: Quick assembly or disassembly without tools.
-
Applications: Furniture, temporary panels, equipment covers.
-
Advantage: Tool-free, fast installation.
4. Cap Nut (Acorn Nut)
Cap nuts, or acorn nuts, feature a dome-shaped top that covers the bolt’s end, offering both protection and a decorative finish. They prevent injury from exposed threads and provide an aesthetically pleasing look. Cap nuts are widely used in furniture, automotive applications, and decorative structures where both safety and appearance matter.
-
Shape: Dome-shaped top to cover bolt end.
-
Use: Decorative and protective; covers sharp bolt ends.
-
Applications: Furniture, automotive, decorative structures.
-
Advantage: Safety and aesthetics.
5. Flange Nut
Flange nuts have a built-in washer-like flange that distributes load over a larger area, reducing material stress. They are commonly used in automotive, machinery, and structural assemblies where even force distribution is crucial. The integrated flange often eliminates the need for a separate washer, simplifying installation while maintaining stability and strength.
-
Shape: Hex nut with integrated washer-like flange.
-
Use: Distributes pressure over a larger surface area.
-
Applications: Automotive, machinery, structural assembly.
-
Advantage: Reduces material stress, often eliminates separate washer.
6. T-Nut
T-nuts are designed for wood applications and feature a flat base with prongs that dig into the material, creating a threaded insert. They are ideal for furniture, wooden fixtures, and jigs, offering strong and hidden threads. T-nuts provide a durable and stable fastening solution while keeping the appearance of the wood clean and smooth.
-
Shape: Flat base with prongs; internally threaded.
-
Use: Provides threaded insert in wood.
-
Applications: Furniture, wooden fixtures, jigs, and woodworking projects.
-
Advantage: Creates strong, hidden threads in wood.
7. Coupling Nut
Coupling nuts are long hex nuts designed to connect two threaded rods, extending their length without welding. They are commonly used in structural rods, scaffolding, and machinery where longer assemblies are needed. Coupling nuts offer a secure and reliable method to join threaded rods, maintaining strength and stability across extended applications.
-
Shape: Long hex nut.
-
Use: Joins two threaded rods together.
-
Applications: Structural rods, scaffolding, machinery.
-
Advantage: Extends threaded rods without welding.
8. Square Nut
Square nuts have four sides instead of six, offering more surface area for tool grip. They are often used with square-headed bolts or in situations where a wrench cannot rotate a hex nut. Square nuts are popular in machinery, antique furniture, and electrical components due to their secure fastening and practical design in tight spaces.
-
Shape: Four-sided nut.
-
Use: Used with square-headed bolts or where a wrench cannot rotate a hex nut.
-
Applications: Machinery, antique furniture, electrical components.
-
Advantage: Offers more surface area to grip with tools.
Nut Sizes
Choosing the correct nut size is essential for creating secure and reliable assemblies. Using the wrong size can lead to loose connections, stripped threads, or even structural failure. Nut sizes are determined by several key factors that ensure compatibility with bolts and the materials being fastened. Understanding these measurements helps you select the right nut for every project, from furniture to heavy machinery.
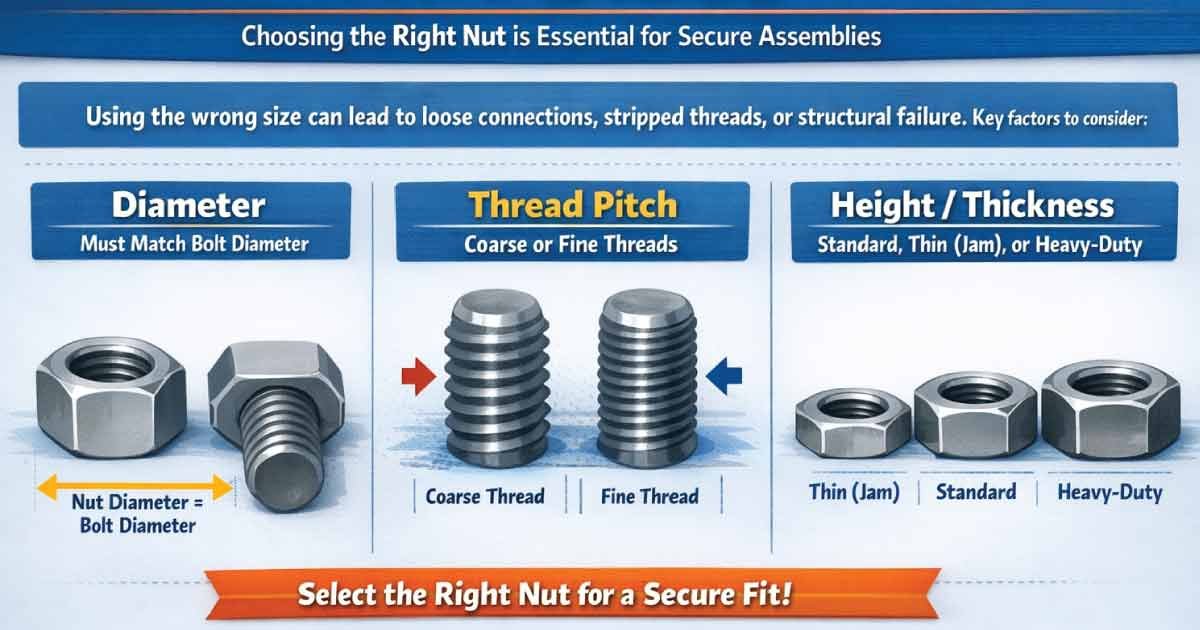
-
Diameter – must match bolt diameter.
-
Thread Pitch – distance between threads (coarse or fine).
-
Height/Thickness – standard, thin (jam), or heavy-duty.
Standard Nut Size Chart
| Nut Type | Bolt Diameter | Thread Pitch (mm) | Height (mm) | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hex Nut | M6 | 1.0 | 5 | Furniture, machinery |
| Hex Nut | M8 | 1.25 | 6.5 | Automotive, brackets |
| Lock Nut | M10 | 1.5 | 8 | Machinery, automotive |
| Wing Nut | 1/4″ | 20 TPI | 10 | Furniture, panels |
| Cap Nut | M12 | 1.75 | 10 | Decorative or protective |
| Flange Nut | 3/8″ | 16 TPI | 8 | Heavy machinery |
| Coupling Nut | M16 | 2.0 | 30 | Rod extensions |
🔹 Tip: Always measure the bolt diameter and thread pitch before selecting a nut. Use a thread gauge for accuracy.
Nut Materials
Nuts come in various materials to meet different strength, durability, and environmental needs. The material choice affects their load-bearing capacity, resistance to corrosion, and overall suitability for specific applications. Selecting the right material ensures long-lasting, safe, and reliable fastening for projects ranging from furniture to heavy machinery.
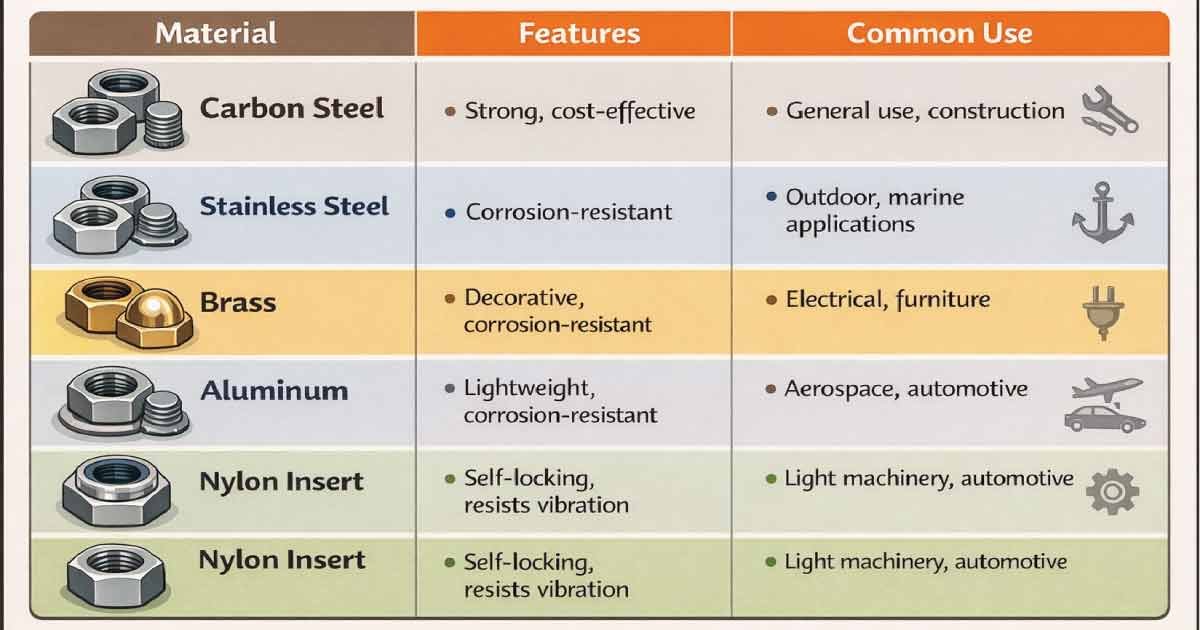
| Material | Features | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Strong, cost-effective | General use, construction |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant | Outdoor, marine applications |
| Brass | Decorative, corrosion-resistant | Electrical, furniture |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Aerospace, automotive |
| Nylon Insert | Self-locking, resists vibration | Light machinery, automotive |
Choosing Nut Material
Selecting the right nut material is essential for strength, durability, and long-term performance. Different materials perform better in specific environments and applications. Choosing correctly ensures your assembly resists rust, handles heavy loads, remains secure under vibration, and even looks aesthetically pleasing. Understanding material properties helps you match the nut to the task for safe and reliable fastening.
-
Outdoor applications: Stainless steel or brass to resist rust.
-
Heavy loads: High-grade steel nuts (Grade 5 or 8).
-
Decorative uses: Brass or cap nuts.
-
Vibration-prone machinery: Nylon insert lock nuts.
Nut Applications and Uses
Matching nuts to the right bolts and materials ensures secure, durable, and safe fastening. Different applications require specific nut types and materials to provide strength, stability, and longevity. Here’s a detailed overview of the main nut applications across various industries and projects.
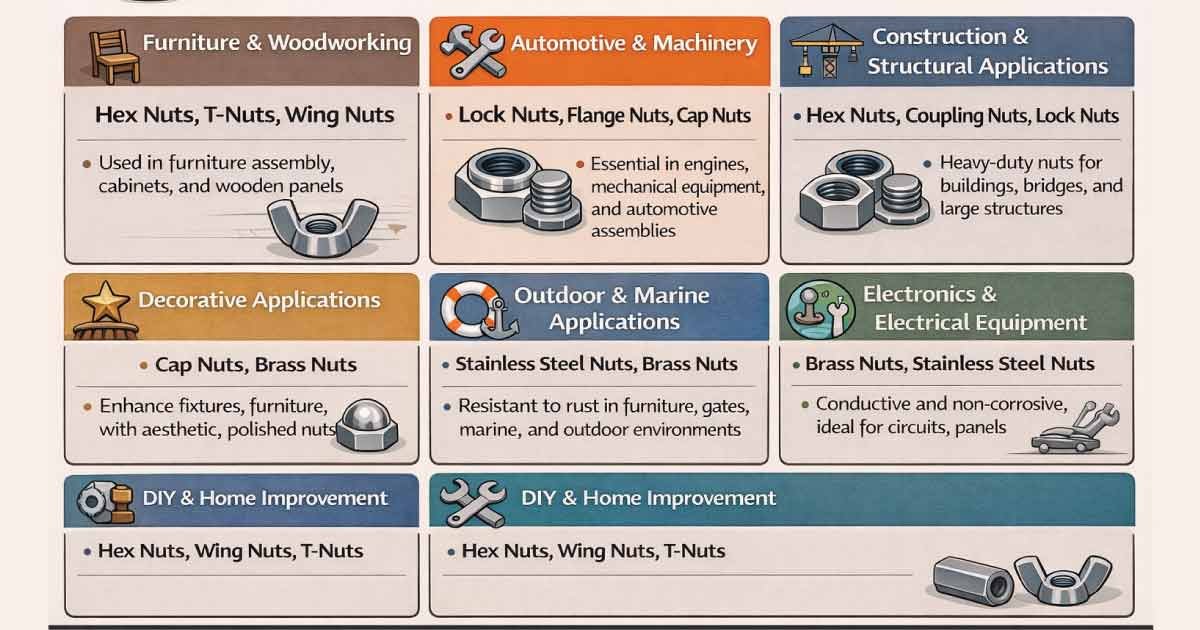
1. Furniture and Woodworking
In furniture and woodworking, nuts are essential for creating sturdy, long-lasting joints. Hex nuts, T-nuts, and wing nuts are commonly used, often with steel or brass. T-nuts in wooden panels provide hidden, durable threads, ensuring a clean look while maintaining strong structural integrity in cabinets, tables, and other wooden assemblies.
2. Automotive and Machinery
Automotive and machinery projects require nuts that resist vibration and heavy loads. Lock nuts, flange nuts, and cap nuts made from high-tensile steel or stainless steel are ideal. These nuts prevent loosening in engines, mechanical equipment, and automotive assemblies, ensuring safety, reliability, and smooth performance under stress and constant motion.
3. Construction and Structural Applications
Construction and structural projects demand heavy-duty nuts to hold large assemblies securely. Hex nuts, coupling nuts, and high-strength lock nuts made of carbon steel or stainless steel provide the necessary load-bearing capacity. Proper matching with bolt grade, along with washers or flanges, ensures stability and prevents structural failures in buildings or machinery.
4. Decorative Applications
Decorative applications require nuts that provide both functionality and aesthetics. Cap nuts and brass nuts, often made from brass or stainless steel, hide exposed threads and enhance the appearance of assemblies. They are used in furniture, fixtures, and decorative hardware to combine safety, neat finishes, and visual appeal without sacrificing strength.
5. Outdoor and Marine Applications
Outdoor and marine projects demand corrosion-resistant nuts that withstand moisture and harsh environments. Stainless steel and brass nuts are commonly used for furniture, gates, marine equipment, and outdoor fixtures. These nuts provide long-lasting performance, resist rust, and maintain structural integrity even under exposure to rain, saltwater, or humidity.
6. Electronics and Electrical Equipment
In electronics and electrical assemblies, nuts must be precise and conductive or non-corrosive. Brass and stainless steel nuts are ideal for circuit boards, panels, and electrical enclosures. They secure components without compromising conductivity, prevent loosening from vibration, and protect delicate equipment from short circuits and environmental damage.
7. DIY and Home Improvement Projects
DIY and home improvement projects require versatile nuts for a variety of tasks. Hex nuts, wing nuts, and T-nuts, often made from steel or brass, are used in furniture assembly, shelving, fixtures, and hobby projects. Selecting the right nut ensures safety, durability, and proper alignment, making assembly easier and more reliable.
Nut Thread Types
Nuts are internally threaded to match bolts or screws, and selecting the correct thread type is critical for secure and reliable fastening. Using the wrong thread can damage hardware, reduce clamping strength, and compromise safety. Understanding coarse, fine, metric, and UTS threads helps ensure proper fit and long-lasting performance in any project.
Coarse Threads: Larger spacing, ideal for wood and soft materials.
Fine Threads: Smaller spacing, suitable for metal and high-strength applications.
Unified Thread Standard (UTS): Common in the USA; uses threads per inch (TPI).
Metric Threads: Standard worldwide; pitch in millimeters.
🔹 Pro Tip: A mismatched thread type can strip both nut and bolt, compromising safety.
Nut Grades and Strength
Nut strength must match the corresponding bolt to ensure proper clamping force and secure fastening. Nut grades indicate their tensile strength, helping you select the right combination for safety, durability, and reliable performance in any application.
| Grade | Material | Minimum Tensile Strength | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Carbon Steel | 74,000 psi | Light-duty construction |
| 5 | Medium Carbon Steel | 120,000 psi | Automotive, general machinery |
| 8 | Medium Carbon Alloy Steel | 150,000 psi | Heavy machinery, load-bearing |
Always pair the nut grade with the bolt grade for maximum reliability.
Washers and Nut Combinations
Washers are commonly paired with nuts to improve fastening performance and protect materials. They help distribute load evenly, prevent loosening under vibration, and safeguard surfaces and finishes. Using the right washer with a nut ensures durability, stability, and a professional finish in both functional and decorative applications.
Distribute load – prevents damage to surfaces.
Prevent loosening – lock washers or spring washers.
Protect finishes – especially in decorative applications.
Quick Reference:
| Nut Type | Washer Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Hex Nut | Flat Washer | Load distribution |
| Lock Nut | Spring Washer | Vibration resistance |
| Cap Nut | Flat Washer | Protect surfaces, aesthetics |
Common Mistakes When Using Nuts
Using nuts incorrectly can lead to stripped threads, loosening, corrosion, or even structural failure. Common mistakes include wrong size, mismatched threads, improper material, skipping washers on soft surfaces, or ignoring nut grades, all of which compromise safety and reliability.
Wrong size nut: Can strip threads or loosen over time.
Mismatched thread pitch: Leads to damaged hardware.
Incorrect material: Can corrode or fail under load.
No washer on soft surfaces: Causes surface indentation.
Ignoring nut grade: Risk of breakage under stress.
🔹 Always double-check nut specifications before assembly.
Tips for Selecting the Right Nut
Choosing the right nut is essential for secure, durable, and safe assemblies. Accurate measurement, understanding the application, and matching nut and bolt strength ensures reliability. Using locking devices and inspecting for damage further prevents loosening and failure, making your fastening projects safer and long-lasting.
Measure accurately: Use calipers for diameter and thread gauge for pitch.
Consider application: Load, vibration, environmental exposure.
Match nut to bolt grade: Strength matters more than cost in critical assemblies.
Use locking devices if necessary: Nylon inserts, lock washers, or threadlike adhesives.
Inspect before use: Check for damaged threads or corrosion.
Conclusion
Nuts may appear simple, but their correct selection is crucial for safety, durability, and performance in any project. Understanding types, sizes, materials, threads, and applications allows you to choose the perfect nut for your project, whether it’s furniture, automotive, machinery, or construction.
By following this complete nut guide, you can confidently assemble components, prevent failures, and even improve the aesthetic and functional quality of your work. Keep this guide as your reference, and you’ll never have to guess which nut to use again.
🔹 Pro Tip: For maximum authority, link this guide to related posts on bolts, screws, fasteners, and washers to create a strong internal linking network that Google loves.

