Heavy hex nuts are widely used in construction, structural steelwork, bridges, heavy machinery, and industrial fastening applications. Compared to standard hex nuts, they offer greater strength, improved load distribution, and better resistance to vibration and loosening. Understanding their definition, dimensions, sizes, and materials helps engineers, contractors, and buyers select the correct fastener for demanding environments.
This guide explains everything you need to know about heavy hex nuts in simple and practical terms.
What Is a Heavy Hex Nut?

A heavy hex nut is a six-sided internally threaded fastener that is thicker and wider across flats than a standard hex nut. It is designed to be used with high-strength bolts where higher clamping force and durability are required.
Heavy hex nuts are commonly paired with structural bolts and are manufactured to meet strict dimensional and mechanical standards such as ASTM, ASME, and ISO.
Key Characteristics
- Thicker profile than standard hex nuts
- Larger bearing surface
- Designed for high-load and structural applications
- Improved resistance to stripping and deformation
Heavy Hex Nut – Definition
A heavy hex nut is a six-sided internally threaded fastener that is thicker and wider than a standard hex nut. It is designed for high-strength and structural applications where greater load-bearing capacity, improved thread engagement, and better resistance to loosening are required.
Heavy hex nuts are commonly used with structural and high-strength bolts in construction, bridges, steel structures, and heavy machinery. Their larger bearing surface helps distribute pressure evenly, reducing the risk of thread stripping or joint failure under heavy loads.
Heavy Hex Nut vs Standard Hex Nut
Although heavy hex nuts and standard hex nuts may look alike, they are designed for different purposes. Heavy hex nuts provide greater strength, thicker profiles, and wider bearing surfaces, making them ideal for structural and high-load applications, while standard hex nuts are suited for general, light-duty fastening needs.
Table: Heavy Hex Nut vs Standard Hex Nut
| Feature | Heavy Hex Nut | Standard Hex Nut |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Thicker | Thinner |
| Width Across Flats | Wider | Narrower |
| Load Capacity | High | Moderate |
| Applications | Structural & heavy-duty | General fastening |
| Cost | Slightly higher | Lower |
What Does a Heavy Hex Nut Look Like?
A heavy hex nut has a solid, six-sided shape that closely resembles a standard hex nut but appears noticeably thicker and wider. Its flat top and bottom surfaces and increased height provide better tool grip and greater thread engagement, resulting in improved strength, stability, and durability in high-stress and structural applications.
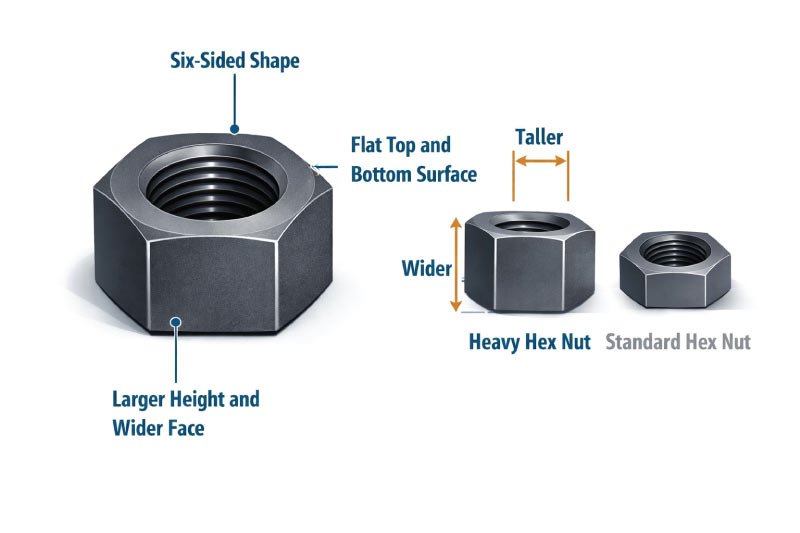
A heavy hex nut has:
- A six-sided (hexagonal) shape
- A flat top and bottom surface
- A larger height and wider face compared to standard nuts
Because of its increased thickness, it provides more thread engagement, which significantly improves strength and durability in high-stress applications.
Heavy Hex Nut Dimensions Explained
Heavy hex nut dimensions determine how accurately the nut fits with bolts and tools. These measurements are standardized to ensure proper alignment, secure fastening, and compatibility across manufacturers. Key dimensions include the nominal diameter, which matches the bolt size, the width across flats for wrench fitting, and the nut’s thickness, which affects strength.
Common Dimensions Include:
- Nominal Diameter – Bolt size the nut fits
- Width Across Flats (WAF) – Distance between two opposite flat sides
- Thickness (Height) – Vertical height of the nut
Heavy Hex Nut Dimensional Overview Table Chart
| Dimension Name | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal Diameter | Thread size (e.g., 1/2″, 3/4″) | Determines bolt compatibility |
| Width Across Flats | Tool grip size | Affects wrench selection |
| Thickness | Nut height | Influences load strength |
| Thread Pitch | Threads per inch | Ensures secure fit |
Heavy Hex Nut Size Chart
Heavy hex nuts are manufactured in both imperial (inch) and metric sizes to match different bolt standards. The inch-size chart below shows commonly used dimensions, helping you select the correct nut based on bolt size, wrench fit, and required thickness for secure and reliable fastening.
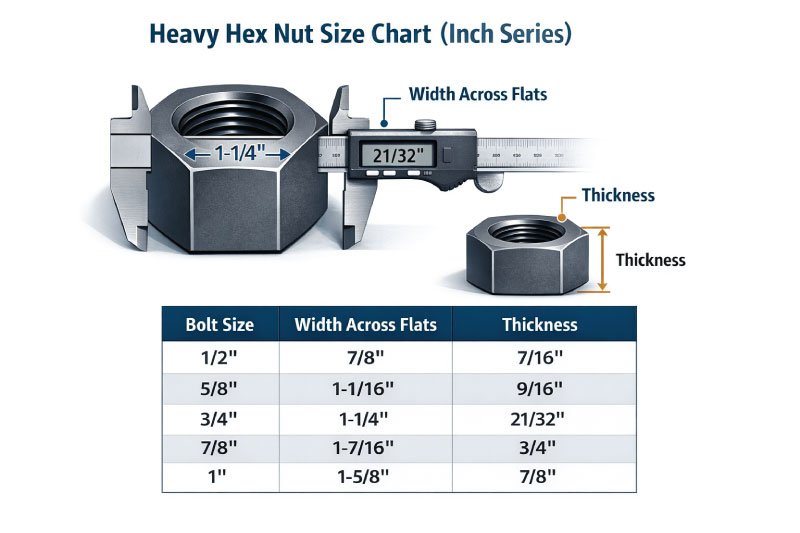
Heavy Hex Nut Size Chart (Inch Series) With Table
| Bolt Size | Width Across Flats | Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 7/8″ | 7/16″ |
| 5/8″ | 1-1/16″ | 9/16″ |
| 3/4″ | 1-1/4″ | 21/32″ |
| 7/8″ | 1-7/16″ | 3/4″ |
| 1″ | 1-5/8″ | 7/8″ |
Note: Dimensions may vary slightly depending on standards such as ASTM A563 or ASME B18.2.2.
Heavy Hex Nut Materials
Material choice plays a major role in determining a heavy hex nut’s strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and application suitability. Selecting the right material ensures the nut performs reliably under load, environmental exposure, and long-term use in structural or industrial projects.
1- Carbon Steel
Carbon steel heavy hex nuts are known for their high strength, affordability, and wide availability. They are commonly used in structural steel, construction, and general industrial applications where high load capacity is needed without excessive cost. They offer reliable performance in controlled environments.
2- Alloy Steel
Alloy steel heavy hex nuts provide exceptional tensile strength, toughness, and resistance to extreme loads. They are ideal for heavy machinery, high-pressure systems, and critical mechanical applications where maximum durability and performance are required under intense stress and vibration.
3- Stainless Steel
Stainless steel heavy hex nuts are valued for their excellent corrosion resistance, clean appearance, and long service life. They are commonly used in outdoor, marine, food-grade, and chemical environments where protection against rust, moisture, and harsh conditions is essential.
4- Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel heavy hex nuts are coated with zinc to provide enhanced rust and corrosion protection. This makes them ideal for construction, outdoor structures, fencing, and exposed environments where moisture and weather conditions could otherwise reduce fastener lifespan.
5- Brass
Brass heavy hex nuts are corrosion-resistant, non-magnetic, and electrically conductive, making them suitable for electrical systems, decorative applications, and environments requiring resistance to rust. They are softer than steel but offer reliable performance in low-load and specialty uses.
6- Heavy Hex Nut Materials Explained With Table
| Material | Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | High strength, economical | Structural steel |
| Alloy Steel | Very high tensile strength | Heavy machinery |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant | Outdoor & marine |
| Galvanized Steel | Rust protection | Construction projects |
| Brass | Non-magnetic, corrosion resistant | Electrical uses |
Grades of Heavy Hex Nuts
Heavy hex nuts are manufactured in different grades to match the strength and specifications of the bolts they are used with. Selecting the correct grade is essential to ensure structural integrity, load-bearing performance, and safety in construction, machinery, and industrial applications. Each grade is designed for specific uses and environmental conditions.
Common Grades:
-
ASTM A563 Grade A – General structural use
-
ASTM A563 Grade DH – High-strength applications
-
ASTM A194 Grade 2H – Used with ASTM A193 bolts
-
ASTM F594 – Stainless steel grade
Choosing the correct grade ensures proper load-bearing performance and safety.
How to Measure a Heavy Hex Nut
Measuring a heavy hex nut accurately ensures proper bolt compatibility, secure fastening, and safe load performance. Using the correct tools and following a simple step-by-step approach helps you identify the exact nut size, thread specifications, and overall dimensions required for structural or heavy-duty applications.

1. Measure the Nominal Diameter
Start by measuring the inside diameter of the nut using a caliper. This measurement identifies the bolt size the heavy hex nut is designed to fit. Accurate diameter measurement is essential to avoid loose fitting or thread mismatch during installation.
2. Check the Thread Pitch
Use a thread pitch gauge to determine the number of threads per inch or the metric thread spacing. Matching the correct thread pitch ensures smooth engagement between the nut and bolt, preventing cross-threading, premature wear, or fastening failure.
3. Measure Width Across Flats (WAF)
Measure the distance between two opposite flat sides of the nut. This width across flats determines the correct wrench or socket size needed for installation and tightening, ensuring proper tool grip and reducing the risk of rounding.
4. Measure the Nut Thickness
Measure the height of the nut from top to bottom. Heavy hex nuts are thicker than standard nuts, and this thickness provides greater thread engagement, improved load distribution, and higher resistance to stripping under heavy tightening forces.
5. Identify the Material and Grade
Check markings, finish, or documentation to identify the nut’s material and grade. Knowing this information helps confirm strength ratings, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with the matching bolt for structural or high-strength applications.
6. Verify the Applicable Standard
Finally, confirm the manufacturing standard, such as ASTM A563 or ASME B18.2.2. Verifying standards ensures dimensional accuracy, load capacity, and compliance with project or safety requirements, especially in construction and industrial environments.
Applications of Heavy Hex Nuts
Heavy hex nuts are widely used in industries where strength, safety, and reliability are critical. Their design allows them to withstand high tension loads, making them ideal for applications that demand secure and durable fastening under extreme conditions. Choosing the right nut ensures long-term performance and structural integrity.
Typical Applications:
-
Structural steel connections
-
Bridges and highway projects
-
Power plants and refineries
-
Heavy equipment assembly
-
Wind and solar installations
Their ability to handle high tension loads makes them essential for critical joints.
Advantages of Heavy Hex Nuts
Heavy hex nuts offer several key advantages that make them ideal for demanding applications. Their thicker design and wider bearing surfaces provide higher load capacity, better tool engagement, and improved structural safety. They also reduce the risk of thread stripping and ensure a longer service life, making them a reliable choice in heavy-duty projects.
Key Advantages:
| Advantage | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Higher Load Capacity | Can handle stronger bolts and heavier forces |
| Better Tool Engagement | Easier and safer to tighten with wrenches or sockets |
| Reduced Risk of Thread Stripping | Less likely to deform under high torque |
| Longer Service Life | Durable for long-term structural applications |
| Improved Structural Safety | Provides reliable fastening for critical joints |
Standards and Specifications
Heavy hex nuts are produced according to established standards to ensure consistency, safety, and compatibility with bolts. These standards define dimensions, mechanical properties, and material requirements, making it easier to select the correct nut for structural, industrial, or heavy-duty applications. Always check the required standard before purchase.
- ASTM A563
- ASTM A194
- ASME B18.2.2
- ISO 4032 (metric equivalents)
Always confirm the standard required for your project before purchasing.
Final Thoughts
Heavy hex nuts play a vital role in structural and industrial fastening. Their increased thickness, wider dimensions, and high-strength materials make them suitable for applications where safety, durability, and load capacity are critical.
By understanding definitions, dimensions, sizes, materials, and standards, you can confidently choose the right heavy hex nut for any heavy-duty application.
👉 Learn all about Wrench Sizes Explained: Tips, Charts & Selection Guide in this detailed post. Understand how to choose the right wrench for every nut and bolt, use charts for accurate sizing, and follow expert tips for safe and efficient work. Read the full guide for precise and hassle-free fastening!

