Hex nuts are among the most widely used fasteners in construction, automotive, machinery, furniture, and DIY projects. Despite their small size, they play a critical role in holding structures together safely and securely.
Understanding hex nut sizes, grades, measurements, and proper usage helps prevent failures and ensures long-lasting assemblies.
This complete guide explains what a hex nut is, how to measure it, different types, common uses, and safe tightening and removal methods—even without a wrench.
What Is a Hex Nut?
A hex nut is a six-sided internally threaded fastener designed to be used with a matching bolt, screw, or threaded rod. Its hexagonal shape allows easy tightening and loosening using standard tools such as wrenches or sockets.
Hex nuts work by clamping two or more components together when threaded onto a bolt. The friction between the nut, bolt, and surface prevents movement and maintains structural integrity.
Hex nuts are available in:
Metric and imperial sizes
Multiple materials (steel, stainless steel, brass)
Different strength grades for light to heavy-duty applications
What Does a Hex Nut Look Like?
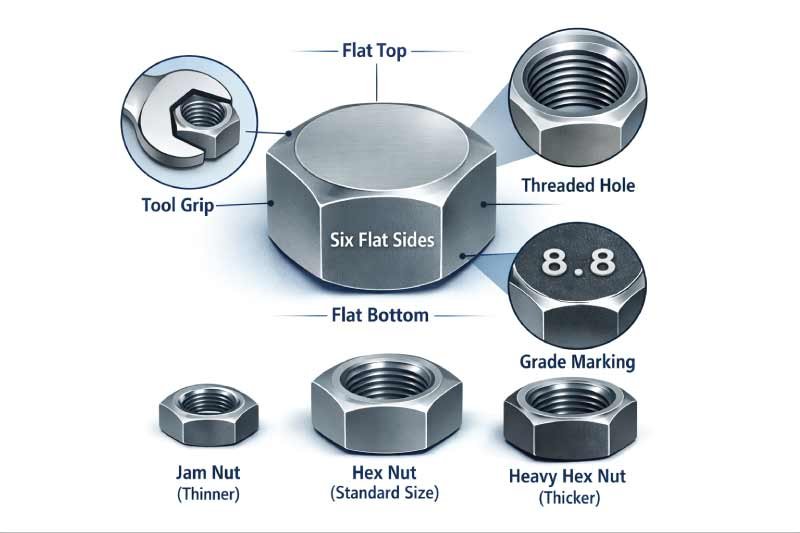
A hex nut is easy to recognize by its simple and practical design. It is a small metal fastener shaped to allow secure tightening with common tools. Understanding what a hex nut looks like helps in identifying the correct type, size, and grade for safe and reliable fastening in any project.
Six flat sides (hexagonal shape)
A central threaded hole
Flat top and bottom surfaces
The flat sides provide grip for tools, while the internal threads match the bolt’s thread size and pitch. Some hex nuts may include markings on the top surface that indicate the material or strength grade.
Visually, hex nuts are compact, symmetrical, and thicker than jam nuts but thinner than heavy hex nuts.
How to Measure Hex Nut Size
Measuring a hex nut accurately ensures it fits the correct bolt, wrench, and application. Proper measurement prevents thread damage, loosening, and safety issues. Hex nut sizing is based on three main factors: thread size, width across flats, and nut thickness.
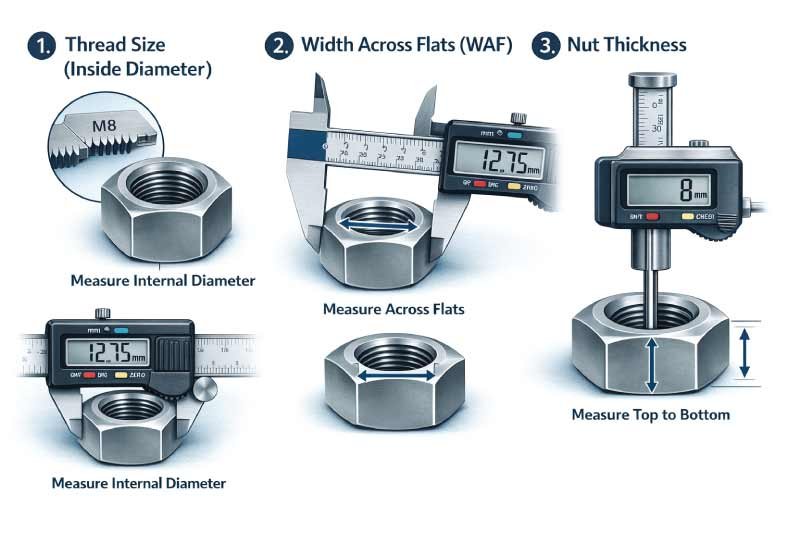
1. Thread Size (Inside Diameter)
Thread size is measured by checking the internal diameter of the hex nut using a caliper or thread gauge. This measurement identifies the correct bolt size, such as M8 or 1/2 inch, ensuring proper thread engagement and a secure, reliable connection.
2. Width Across Flats (WAF)
Width across flats is the distance between two opposite flat sides of the hex nut. This measurement determines the correct wrench or socket size, helping avoid rounding the nut edges and ensuring safe, efficient tightening or loosening during installation or maintenance.
3. Nut Thickness
Nut thickness is measured from the top surface to the bottom surface of the hex nut. Thickness affects clamping strength and load distribution and helps distinguish between standard hex nuts, thinner jam nuts, and thicker heavy hex nuts used in structural applications.
Hex Nut Measurement Table (Metric)
| Nut Size | Thread Diameter | Width Across Flats | Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|
| M6 | 6 mm | 10 mm | 5 mm |
| M8 | 8 mm | 13 mm | 6.5 mm |
| M10 | 10 mm | 17 mm | 8 mm |
| M12 | 12 mm | 19 mm | 10 mm |
What Is a Heavy Hex Nut? (Definition)
A heavy hex nut is a thicker and wider version of a standard hex nut, designed for high-load and structural applications. Its increased bearing surface provides greater strength, improved load distribution, and better resistance to loosening.
Heavy hex nuts are commonly used in structural steel connections, bridges, oil and gas equipment, and heavy machinery, and are typically paired with high-strength bolts.
What Is a Hex Jam Nut?
A hex jam nut is a thinner version of a standard hex nut, mainly used to lock another nut in place. It does not provide primary clamping force but prevents loosening caused by vibration, ensuring stability in threaded assemblies.
Jam nuts are often used:
In pairs with standard hex nuts
In applications with limited space
As locking nuts on threaded rods
Because of their reduced thickness, jam nuts should not be used alone in high-load applications.
What Is a Hex Nut Used For?
Hex nuts are essential fasteners used to secure bolts in a wide range of applications, from construction and industrial machinery to automotive systems and furniture assembly. They provide strong clamping force, easy installation, and reusability. Selecting the right size and grade ensures safety, stability, and long-lasting performance in any project.
Construction framing and steel structures
Automotive engines and suspension systems
Industrial machinery and equipment
Furniture assembly
Home repair and DIY projects
They provide:
Strong clamping force
Easy installation and removal
Reusability
Choosing the correct nut size and grade ensures safety and long-term performance.
Hex Nut Grades Explained
Hex nuts are categorized by strength grades, which indicate their load-bearing capacity, hardness, and suitable applications. Choosing the correct grade ensures structural integrity and prevents failures.
Higher grades offer greater strength but less flexibility, while lower grades are suitable for light-duty uses, making proper selection essential for safety and performance.
Common Hex Nut Grades Table
| Grade | Material | Strength Level | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 2 | Low-carbon steel | Low | Furniture, light-duty |
| Grade 5 | Medium-carbon steel | Medium | Automotive, machinery |
| Grade 8 | Heat-treated steel | High | Heavy-duty, structural |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant steel | Medium | Outdoor, marine |
Higher grades are stronger but less flexible, making correct selection critical.
How to Tighten a Hex Nut
Properly tightening a hex nut is essential for a secure and reliable connection. Correct technique ensures the bolt and nut hold components firmly without causing damage.
Using the right tools, applying even torque, and avoiding overtightening are key to preventing stripped threads or joint failure in any application.
To tighten a hex nut properly:
Place the nut onto the bolt by hand
Turn clockwise until snug
Use a wrench or socket to tighten further
Apply torque evenly—do not overtighten
For critical applications, use a torque wrench to meet manufacturer specifications. Overtightening can strip threads or cause bolt failure.
How to Remove a Hex Nut
Removing a hex nut may seem simple, but doing it correctly prevents damage to both the nut and the surrounding components. Using the right tools and techniques ensures safety, efficiency, and prevents stripping or rounding of threads. Follow these steps to remove a hex nut effectively, even if it is stuck or rusted.
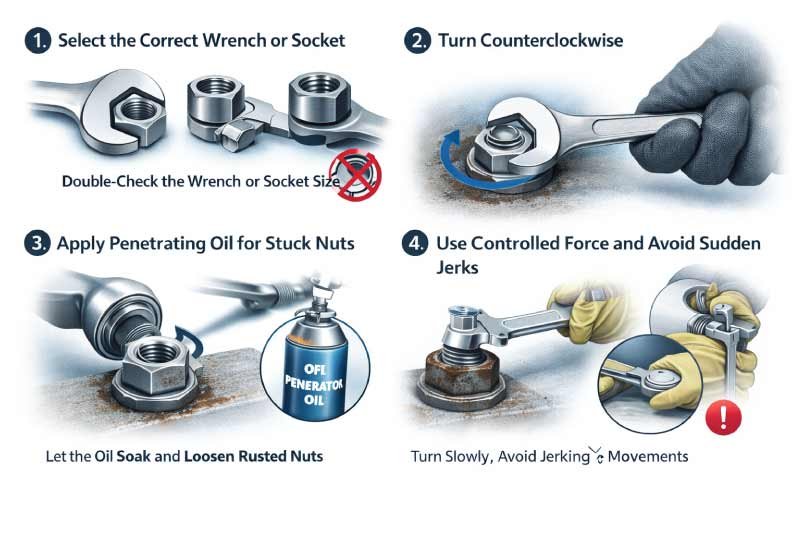
1. Select the Correct Wrench or Socket
Choosing the correct size wrench or socket is crucial for safe and effective hex nut removal. Using an incorrectly sized tool can round the nut corners, making it difficult to remove and potentially damaging the bolt or surrounding material. Always double-check the size before applying force.
2. Turn Counterclockwise
To loosen a hex nut, turn it counterclockwise. Apply steady and controlled pressure to avoid slipping or damaging the nut. Maintaining consistent motion ensures the threads disengage smoothly, reducing the risk of injury or stripping the nut during the removal process.
3. Apply Penetrating Oil for Stuck Nuts
If the hex nut is rusted or stuck, apply penetrating oil to the threads. Let it soak for several minutes to reduce friction and corrosion. This helps the nut loosen more easily when you turn it with a wrench, preventing excessive force and potential damage.
4. Use Controlled Force and Avoid Sudden Jerks
When loosening a hex nut, use slow, controlled force rather than sudden jerks. Abrupt movements can damage tools, warp the nut, or injure your hands. Patience and steady pressure ensure safe removal while protecting both the fastener and the surrounding components.
How to Remove a Hex Nut Without a Wrench
Sometimes, a wrench may not be available, but a hex nut can still be removed using alternative methods. Careful application of these techniques prevents damage to the nut, bolt, or surrounding components. Always proceed slowly and cautiously, especially for rusted or tightly fastened nuts.

1. Use Pliers or Locking Pliers
For small or moderately tight hex nuts, pliers or locking pliers can provide enough grip to turn the nut. Position the tool firmly on the flat sides, apply steady pressure, and rotate counterclockwise. This method works well for low-torque applications but may struggle with larger or heavily tightened nuts.
2. Adjustable Wrench Substitute (Vise Grips)
If a wrench is unavailable, vise grips can act as a temporary substitute. Clamp the grips securely onto the hex nut and turn slowly. Ensure a tight grip to prevent slipping or rounding the corners of the nut. This method is ideal for medium-sized nuts with moderate torque.
3. Hammer and Chisel Method
For stuck or rusted hex nuts, a hammer and chisel can be used to tap the nut counterclockwise. Place the chisel at the edge of the nut and gently tap with the hammer to loosen it. This requires precision to avoid damaging the nut, bolt, or surrounding material.
4. Two-Nut Locking Method on Threaded Rods
On threaded rods, the two-nut locking method can help remove a stuck nut without a wrench. Thread a second nut against the first and tighten them together. Then use pliers or other tools on the outer nut to turn both simultaneously, providing leverage to loosen the stuck nut safely.
How to Unscrew a Hex Nut
Unscrewing a hex nut may seem simple, but doing it correctly ensures safety and prevents damage to the bolt, nut, or surrounding components. Following proper techniques allows smooth removal, even for rusted or stuck nuts, while avoiding stripped threads and injuries.
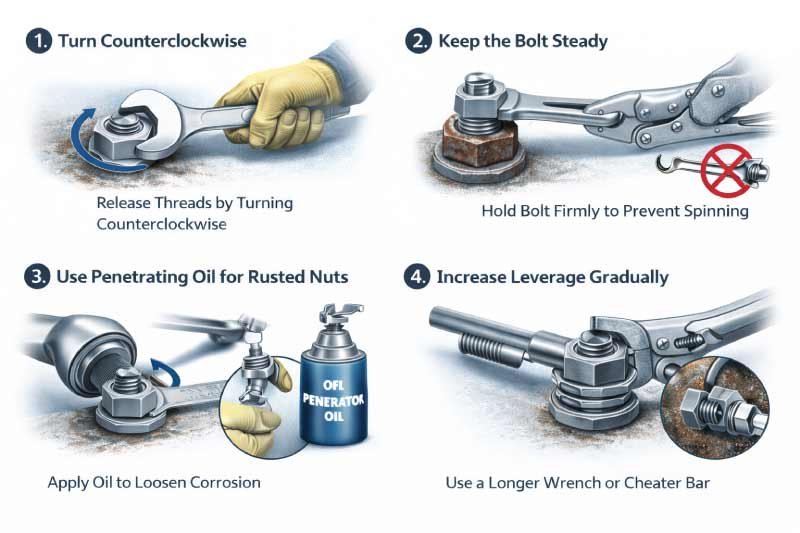
1. Turn Counterclockwise
To unscrew a hex nut, always turn it counterclockwise. This standard direction releases the threads from the bolt gradually. Apply steady and controlled pressure to avoid slipping, rounding the nut corners, or damaging the bolt threads during the process.
2. Keep the Bolt Steady
If possible, hold the bolt firmly in place while turning the nut. This prevents the bolt from rotating along with the nut, ensuring the threads disengage properly. Using a second wrench or pliers to stabilize the bolt can make the process easier and safer.
3. Use Penetrating Oil for Rusted Nuts
For stuck or rusted hex nuts, apply penetrating oil to the threads. Allow it to soak for several minutes to reduce friction and loosen corrosion. This helps the nut turn more easily and prevents excessive force that could damage the nut or bolt.
4. Increase Leverage Gradually
If the nut is particularly tight, gradually increase leverage by using a longer wrench, pipe extender, or cheater bar. Apply steady, controlled pressure rather than sudden force to prevent slipping or rounding the nut corners. Slow, consistent motion is safer and more effective.
5. Check for Stripped or Rotating Bolts
If the hex nut spins freely without loosening, the bolt may be stripped or rotating with the nut. In such cases, inspect the threads carefully. You may need to stabilize the bolt, replace damaged components, or use specialized tools to remove the nut safely.
Hex Nut Wrench Size Chart
Knowing the correct wrench size for a hex nut is essential for safe and efficient fastening or removal. Using the right tool prevents rounding the nut corners, reduces damage to bolts, and ensures proper torque application. Below is a quick reference for common hex nut sizes in both metric and imperial measurements.
| Nut Size | Wrench Size (Metric) | Wrench Size (Imperial) |
|---|---|---|
| M6 | 10 mm | 3/8″ |
| M8 | 13 mm | 1/2″ |
| M10 | 17 mm | 11/16″ |
| M12 | 19 mm | 3/4″ |
Using the correct wrench size prevents rounding the nut corners.
Final Thoughts
Hex nuts may seem simple, but choosing the right size, grade, and type makes a significant difference in safety and performance. Whether you’re assembling furniture, repairing a vehicle, or working on heavy equipment, understanding how hex nuts work helps you achieve reliable, professional results.
With proper measurement, correct tightening, and safe removal techniques, hex nuts will continue to be one of the most dependable fasteners in any project.
Also Read:
👉 Discover everything you need to know about Nut Size Chart: Types, Materials and Applications in this comprehensive guide. Learn how to choose the right nut size, understand different materials, and explore their practical uses. Whether for DIY, construction, or machinery, this post helps you select the perfect nut for every project—read the full guide now!

